
CELL DIVISION AND CELL CYCLE
DEFINITION
-
According to cell theory “ALL CELLS ARISE FROM PRE-EXISTING CELLS” that means all the new cell are formed from the old cells .
-
The formation of new cells from the old cells through series of sequential changes is called CELL DIVISION.
-
All the cells in eukaryotic organisms divide except RBCs , nerve cells and some muscles cells
-
Nucleus plays an important role in cell division as The chromatin threads present in nucleus changes into chromosomes at the time of cell division
-
Centrosome in animal cell and microtubules in plant cell initiates the cell division.
WHY DO CELLS DIVIDE?
-
Cells divide for the growth of an organism
-
To repair the worn out cell and replace dead cells.
-
For reproduction ( formation of gametes)
Cell division consist of two steps:
-
Karyokinesis – Division of nucleus is called karyokinesis.
-
Cytokinesis – Division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis.
“CYTOKINESIS TAKES PLACE AFTER KARYOKINESIS”
CELL CYCLE
The period from the end of first cell division to the next division is called cell cycle.
Cell cycle consist of four phases:-
-
G1 PHASE
-
S PHASE
-
G2 PHASE
-
M PHASE
G1, S AND G2 PHASE ARE KNOWN AS “INTERPHASE” AND M PHASE IS KNOWN AS “DIVISION PHASE”
I] INTERPHASE : it is growth period between two successive divisions of the cell. Synthesis of DNA , RNA , proteins , energy production and growth of a cell takes place in this phase
During this stage cell is prepared for cell division. In order to move from interphase into division phase or mitotic phase many external and internal conditions must be met.
The three sub stages of interphase are :
-
G1 PHASE ( FIRST GAP) – It is the longest period and a period of maximum growth of the cell . In this stage cell accumulate building block of DNA and active proteins , RNA is synthesised with sufficient accumulation of energy reserves for the completion of cell cycle.
-
S PHASE ( SYNTHESIS PHASE) - In this phase duplication of DNA takes place.
-
G2 PHASE ( SECOND GAP) – cytoplasmic growth occurs in this phase which includes growth of many cell organelles. After complete growth cell enters into mitotic phase or M PHASE.
II] M PHASE: In this phase cell divides to from new cells. mitosis occurs in somatic and reproductive cells whereas meiosis occurs in reproductive cells.
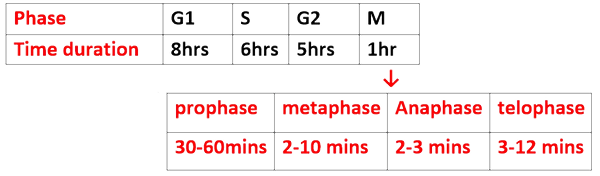
DURATION OF CELL CYCLE
-
In most of the animal and plant cells the entire cel cycle is completed in one day or less.
-
A typical cell cycle takes about 20 hours
-
Usually the time duration of S and G2 is constant , variations are most likely to occur in G1 phase which may be as short as a few hours or may take days or even weeks.
Mitosis
-
Mitosis is the process that divides newly formed chromosomes equally into two daughter cells
-
The term mitosis was given by Flemming in 1880
All the changes that undergone by the cell during mitosis are divisible into four main phases-
-
Prophase
-
Metaphase
-
Anaphase
-
Telophase
PROPHASE : IT IS THE LONGEST PHASE OF MITOSIS. FOLLOWING CHANGES OCCURS DURING THIS PHASE:
-
Chromatin fibres disappears and chromosomes appear
-
Short radiating fibres appear around the centrosome called astral rays that forms aster ( star like ).
-
Centrosome having astral rays divides into centrioles.
-
Each centriole moves opposite side at the poles of the nucleus and forms spindle fibres.
-
Nuclear membrane disappears at the end of prophase .

METAPHASE : It is the short phase. In this phase chromosome come to lie at the equatorial plane .

ANAPHASE : This phase is of shortest duration . During this phase following change takes place:
-
Centrosome splits and chromosome gets divided into its chromatids
-
Each chromatid of chromosome moves towards its opposite side towards pole.
-
At the end of anaphase chromatids reaches the poles which later gets surrounded by nuclear membrane in telophase stage.

TELOPHASE : It is the final stage of mitosis. During this phase following changes takes place:
-
Spindle fibres disappears and nuclear membrane re-appears at each pole surrounding the chromatids forming two daughter nuclei. [KARYOKINESIS]
-
Unfolding, unlooping and uncoiling of chromosomes occurs forming chromatin threads.
-
Cell furrow appears on the cell membrane which later deepens and divides the cytoplasm of the cell forming two daughter cells. [ CYTOKINESIS]

SIGNIFICANCE OF MITOSIS
-
Mitosis is known as Equational division. The daughter cells produced is exactly similar to the parent cell
-
It is responsible for growth , repair and replacement of worn-out and dead cells.
-
It helps in maintaining genetic continuity.
MEIOSIS
Meiosis is a type of cell division in which chromosome divides once and nucleus divides twice resulting in the formation of four daughter cells with haploid set of chromosomes.
Meiosis is a reductional division in which diploid set of chromosomes changes into haploid set. Meiosis occurs in Reproductive cells for the formation of sex cells i.e sperma and ovum.
STAGES OF MEIOSIS (TWO DIVISIONS)
During Meiosis cell divides twice.
-
First division Meiotic division in which reduction division , chiasmata formation and crossing over takes place.
-
Second division is similar to the mitosis in which no reduction division take place
EVENTS THAT TAKES PLACE DURING MEIOSIS
During meiosis, prophase , metaphase , anaphase and telophase occurs twice . One in meiotic I and second in Meiotic II.
Prophase of first Meiotic division is divided into 5 sub stages.
Leptotene
Zygotene
Pachytene
Diplotene
Diakinesis
SYNAPSIS: During the zygotene stage of prophase I the homologous chromosomes come to lie opposite to each other . Thus the pairing of homologous chromosome is called Synapsis and a pair is called Bivalent
CHIASMATA FORMATION AND CROSSING OVER: During Diplotene and pachytene stage of Prophase I the bivalent chromatids tends to separate and changes into four chromatids (tetrad) " The non sister chromatids overlap each other due to which exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatids take place . This phenomenon is called as Crossing over. "
SIGNIFICANCE OF MEIOSIS
-
Meiosis maintains the number of chromosomes in the species
-
It is responsible for the reduction of chromosomes to half in the daughter cells
-
Meiosis brings about the variations in species due to exchange of genes during crossing over.
SIGNIFICANCE OF CROSSING OVER
-
Exchange of genetic material between Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes takes place during crossing over
-
It brings about variations due to exchange of genetic material.

